Understanding Types of Positioning

In a world filled with countless brands competing for attention, what makes some businesses stand out while others fade into obscurity? The answer lies in positioning—a simple marketing principle that dictates how a brand, product, or service is perceived. It’s not just about selling a product; it’s about creating a perception, an identity, and an emotional connection.
Think about all the brands like Apple and Nike. What comes to mind when you hear these names? Apple is synonymous with innovation and premium technology, while Nike represents empowerment and sports excellence. Why do we think like this about them? It is merely that they have positioned themselves in a way that is appealing to their target markets.
In this article, we’ll break down the concept of positioning, why it matters, different positioning strategies, and how businesses can integrate positioning into their marketing approach.
What is Positioning?

Marketing positioning is a strategic process for defining and building a differentiated and distinct identity for a brand, product, or service in consumers' minds. It is a process of shaping perceptions to create a distinct and compelling image that differentiates a brand from competitors. Positioning goes beyond physical qualities like product features or price—it is about values, associations, experience, and emotions that resonate with a target audience.
The role of positioning is to place a perception in consumers' minds so that they are aware of what the brand's unique value propositions are and why to pick it over alternatives. This is done through responding to significant questions such as:
- What makes the brand distinctively different from competitors?
- Why should consumers choose the brand over alternatives?
- What specific emotions, values, or benefits does the brand uniquely represent?
Effective positioning influences all business functions, ranging from product design to pricing to advertising communication, customer service, and brand message. By positioning themselves in a strategic way, companies can establish a lasting impression, establish an emotional connection, and develop customer loyalty.
Example of Positioning Strategy
Nike employs a number of positioning strategies to build itself as a market leader in sportswear. The brand highlights its dedication to empowering athletes with innovative, high-performance wear. Nike's positioning is built around the famous line "Just Do It," urging individuals to push themselves and strive for greatness.
Through a relationship with elite athletes and an emphasis on attributes like endurance, strength, and triumph, Nike articulates a specific value proposition: that their products are not just sportswear, but rather performance enhancers and drivers of individual success.
Why is Positioning Essential?
Positioning is a strategic marketing technique that allows businesses to stand out, establish a brand identity, and create lasting customer relationships. Positioning holds substantial importance for multiple compelling reasons:
- Standing Out in a Saturated Marketplace: Effective positioning enables brands to distinguish themselves amid fierce competition by showcasing their distinctive characteristics, core values, and consumer advantages. This strategic differentiation enhances brand recognition and memorability, securing consumer attention in overcrowded markets.
- Building Consumer Trust and Loyalty: A good positioning strategy resonates with consumers and creates a sense of trust and emotional connection. When consumers share a brand's values, lifestyle, or aspirations, they will be more likely to remain with them. Consistent and authentic positioning reinforces those relationships and creates engagement for the long term.
- Justifying Pricing Strategies: Positioning directly affects how consumers see a product's value in proportion to price. Luxury brands justify a premium price tag with positioning on the basis of quality, and low-priced brands appeal to price-sensitive consumers with value-based positioning.
- Ensuring Consistent Messaging: A solid positioning strategy is the foundation for all types of marketing communication to deliver consistent, understandable, and effective messages in advertising, social networking, packaging, and customer service. Strong positioning allows brands to avoid confusing messages that weaken their identity.
- Targeting the Right Audience: Positioning allows brands to locate and target the right audience groups to ensure that advertising is being directed to consumers who will most likely engage with the brand. Strategically positioned brands capture greater market share and significantly influence purchasing decisions.
- Market Penetration and Competitive Advantage: A strong positioning strategy enables brands to effectively penetrate the market by appealing to a well-defined audience. It also creates a competitive edge by establishing the brand as the preferred choice in its category.
Types of Positioning in Marketing
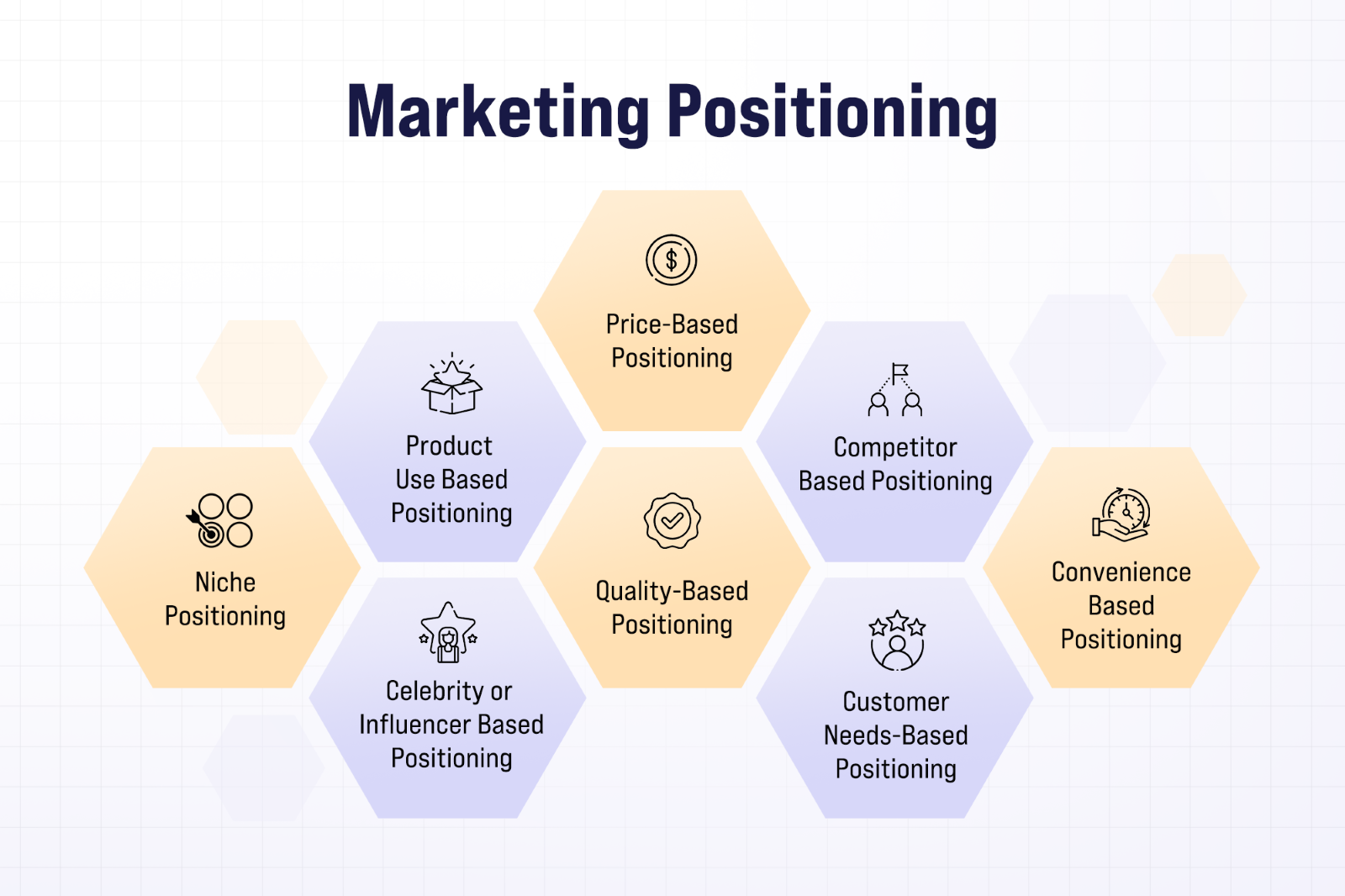
There are various positioning strategies used to communicate a brand’s unique value proposition, ensuring it resonates with specific consumer segments. Let's examine various positioning strategies utilized in contemporary marketing, accompanied by real-world illustrations.
Price-Based Positioning
This strategy positions a brand based on its pricing structure, either as a cost-effective, budget-friendly option or as a premium, high-value alternative. Businesses leveraging this approach focus on attracting price-sensitive customers or those seeking exclusivity and luxury.
Example:
- Affordable Positioning: Jio revolutionized India’s telecom industry by offering low-cost data plans and free calls, making high-speed internet accessible to the masses.
- Premium Positioning: Rolex justifies its high price through craftsmanship, prestige, and exclusivity, appealing to an elite clientele.
Quality-Based Positioning
Brands using quality-based positioning emphasize superior craftsmanship, durability, and performance to justify their value. This approach appeals to customers who prioritize reliability and high standards over cost.
Example:
- Toyota has built its reputation in India as a brand known for durability, reliability, and low maintenance costs, making it the preferred choice for long-term vehicle ownership.
Competitor-Based Positioning
This strategy involves directly comparing a brand with its competitors, highlighting key differentiators and advantages. It allows businesses to position themselves as the superior alternative by addressing gaps or shortcomings in competing products.
Example:
- Pepsi in India positions itself as the younger and cooler alternative to Coca-Cola by using vibrant marketing campaigns featuring Bollywood celebrities, whereas Coca-Cola focuses on nostalgia and tradition.
Convenience-Based Positioning
Convenience-centric positioning emphasizes accessibility, intuitive user experience, and quick service delivery. Brands adopting this strategy ensure that their products or services provide a seamless and efficient experience, catering to consumers who prioritize time and effort savings.
Example:
- Swiggy and Zomato have positioned themselves as fast and reliable food delivery services, ensuring customers get meals with minimal effort and wait time.
Customer Needs-Based Positioning
This approach targets specific pain points or requirements of a particular audience segment. It involves offering solutions tailored to consumer needs, making the brand an indispensable choice in addressing market challenges.
Example:
- Paytm gained prominence in India during demonetization, positioning itself as the ideal platform for cashless transactions, online payments, and digital wallets, making everyday transactions seamless.
Product Use-Based Positioning
Product use-based positioning highlights the various applications or functionalities of a product. This strategy aligns the brand with specific activities or user scenarios, catering to a well-defined group of consumers.
Examples:
- GoPro positions itself as the best action camera for adventure enthusiasts, emphasizing capturing high-action moments like surfing, mountain biking, and skiing.
Celebrity or Influencer-Based Positioning
This positioning strategy leverages endorsements from well-known figures to enhance credibility, trust, and brand awareness. Associating with celebrities or influencers helps businesses establish an aspirational appeal and strengthen consumer connections.
Example:
- Lux has built its image around glamour and beauty by featuring Bollywood celebrities like Kareena Kapoor and Priyanka Chopra in its advertisements.
Niche Positioning
Niche positioning focuses on serving a specialized, highly targeted market segment with unique preferences or requirements. It enables brands to dominate a specific category by offering exclusive, tailored solutions that cater to a distinct audience.
Example:
Royal Enfield has positioned itself as the go-to brand for motorcycle enthusiasts who value adventure and road trips. Its branding focuses on ruggedness, individuality, and freedom.
What is Brand Positioning?
Brand positioning is a strategic marketing technique that defines a brand’s unique value and identity in the marketplace. It articulates a brand's essence, highlights its competitive advantages, and justifies why it represents the best choice for its intended demographic.
At its core, brand positioning is about shaping consumer perceptions in a way that aligns with their needs and desires, ultimately influencing their purchasing decisions. A strong brand positioning strategy fosters long-term customer relationships by making the brand synonymous with values, qualities, or solutions that resonate with consumers.
Brand Positioning Strategy Key Elements
- Target Demographic Analysis: Comprehensive understanding of your intended audience constitutes a fundamental prerequisite for successful positioning. By identifying key demographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors, businesses can tailor their offerings and messaging to appeal to their customers.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyzing competitors allows businesses to identify their strengths and weaknesses, uncover differentiation opportunities, and establish a distinct market position. This insight enables you to position your brand uniquely, highlighting what makes you stand out in a crowded market.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Your USP defines what sets your brand apart from others. It highlights the unique feature, benefit, or value that no competitor offers, making your brand the preferred choice for your target audience.
- Brand Commitment: The brand commitment represents the pledge your brand extends to its customers. It should be compelling and reflect the core values and mission of your brand, ensuring customers know what to expect from their experience with you.
- Brand Personality: A brand’s personality consists of the human-like traits it embodies. Cultivating a robust brand personality facilitates emotional connections with consumers, enhancing relatability and ensuring lasting brand impressions.
- Brand Positioning Declaration: This represents a concise statement defining the brand's specific niche within the marketplace. It communicates who the brand is, what it offers, and what makes it unique, serving as a foundation for consistent messaging across all marketing campaigns.
In essence, brand positioning is the foundation of a brand strategy, as it helps carve out a unique niche for a brand in a competitive market and shapes consumer perceptions, fostering brand loyalty and preference over time.
What is a Perceptual Positioning Map?
A Perceptual Positioning Map serves as a graphical instrument helping companies comprehend how consumers view their offerings relative to competitive alternatives. It provides a market overview by mapping brands along two axes—typically based on key attributes such as price, quality, or performance. This tool helps companies identify gaps or opportunities for differentiation in the market.
To create a perceptual map, businesses gather data from customer feedback, surveys, or market research. The information is then plotted on a graph, with one key attribute (e.g., price) on the horizontal axis and another (e.g., quality) on the vertical axis. Brands positioned farther from the center show stronger differentiation in consumer perception.
Why It’s Useful
- Understand Consumer Perceptions: Helps brands see how they are viewed compared to competitors.
- Identify Opportunities: Highlights gaps in the market where a brand can establish a stronger presence.
- Make Strategic Decisions: Helps enterprises modify their positioning approaches to better reflect consumer expectations and preferences.
- Track Progress: Allows brands to monitor how well their positioning efforts are working overtime.
Integrating Positioning into Marketing Strategy
Integrating positioning into your marketing strategy involves a careful approach to align your brand’s unique value proposition with the needs and expectations of your target audience. Here’s how you can effectively incorporate positioning into your overall marketing plan:
- Understand Your Audience: Conduct in-depth market research to analyze audience behaviors, values, and preferences. This helps craft tailored messaging and offerings that truly resonate with them.
- Conduct Market Research: Study competitors and market gaps to identify unique positioning opportunities and areas where your brand can stand out. Identify areas where competitors demonstrate weaknesses or where consumer demands remain unfulfilled, then leverage these insights to develop distinctive positioning strategies
- Ensure Consistent Messaging: Align all brand communications, from ads to packaging, with your positioning to create a cohesive and recognizable brand identity. Clear, unified messaging helps reinforce your brand’s identity and ensures that consumers immediately recognize and relate to the value you offer.
- Evolve and Adapt Over Time: Regularly reassess your positioning strategy to stay relevant and responsive to market shifts and evolving consumer preferences. Periodically reassessing and refining your strategy will keep your brand relevant and compelling to your audience over time.
FAQ’s
Q1. What are the 3 Cs of strategic positioning?
Ans: The 3 Cs of strategic positioning are:
- Customer: Understanding consumer needs, wants, and pain points through research.
- Channel: Leveraging sales team insights to understand customer profiles and purchasing behavior.
- Competition: Analyzing competitor offerings to identify differentiation opportunities and position the brand uniquely.
Q2. What are the 5 PS of positioning?
Ans: The 5 Ps of positioning include:
- Product: Unique attributes and features of the offering.
- Price: The brand’s perceived value in the market.
- Place: Where and how the product is available to consumers.
- Promotion: Marketing, advertising, and branding efforts.
- People: Customer interactions and service quality
Summing Up
In conclusion, positioning is a powerful strategy that enables brands to stand out in a competitive market by shaping consumer perceptions and building emotional connections.
By understanding their target audience, analyzing competitors, and defining a unique value proposition, businesses can position themselves effectively to capture consumer attention, build loyalty, and drive long-term success.
With the right positioning strategy, brands can carve out a distinct space in the market, resonate with their audience, and stand out from the competition.





