Is Supply Chain Management a Good Career?

Supply Chain Management (SCM) has emerged as a critical field due to a steep rise in global trade expansion and businesses becoming more interconnected. It is an essential and dynamic field that keeps products running smoothly; from manufacturing to logistics, to inventory management, and distribution, supply chain plays a crucial role in ensuring businesses and consumers get the products they need.
But is supply chain management a good career choice? If you’re a student or professional exploring career opportunities, this article will help you understand the potential of SCM as a profession.
What is Supply Chain Management?

Supply Chain Management (SCM) encompasses the strategic oversight of all activities involved in creating and delivering goods and services, from procuring raw materials to ensuring the end product reaches customers. It facilitates the smooth movement of materials, data, and finances across a worldwide network of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
Their responsibilities also include:
- Overseeing inventory management
- Logistics and distribution
- Managing relationships with suppliers and vendors
- Improving operational efficiency
- Reducing waste and unnecessary expenses
- Enhancing customer satisfaction
According to the Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals (CSCMP), SCM harmonizes supply and demand management both within and between organizations, making it a vital function for achieving business success in today’s globally connected economy. Companies across all industries, including retail, healthcare, technology, and manufacturing, rely on SCM to maintain efficiency and profitability.
The Basic Components of Supply Chain Management
To achieve efficiency and optimize operations, SCM consists of several core components that work together to maintain productivity, reduce costs, and meet customer expectations. Below are the five fundamental components of supply chain management.
Planning
Effective supply chain management begins with strategic planning. This stage involves analyzing market trends, predicting customer demand, and aligning production capabilities with business goals. Organizations must evaluate their resources, pinpoint potential obstacles, and create backup strategies to address unexpected disruptions.
Poor planning can lead to overproduction, resource shortages, and increased operational costs. Cutting-edge digital tools like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems empower organizations to optimize operational workflows, enabling intelligent, data-fueled strategic decision-making across supply chain ecosystems.
Sourcing
Sourcing, or procurement, focuses on identifying and securing raw materials, components, and other resources needed for production. Cultivating robust, strategic partnerships with dependable vendors forms the cornerstone of maintaining superior product quality, operational consistency, and competitive cost efficiency.
Companies should assess suppliers based on their ability to meet delivery timelines, maintain quality benchmarks, and provide competitive pricing. A well-organized sourcing strategy includes negotiation, risk assessment, and contingency planning to prevent supply chain disruptions caused by material shortages or supplier failures.
Production
The production stage involves converting raw materials into finished goods through processes such as assembly, testing, quality checks, and packaging. Operational efficiency during production is critical for meeting customer needs while reducing expenses and waste.
Businesses must implement rigorous quality control measures to guarantee that their final products comply with industry standards and satisfy customer expectations. Optimizing production also involves monitoring equipment usage, workforce efficiency, and inventory levels to maintain high productivity and minimize delays.
Distribution
After manufacturing, products must be distributed to customers or retailers in a timely and cost-effective manner. The distribution process involves warehousing, order fulfillment, logistics, and transportation management. A robust distribution network guarantees that products are delivered to their intended locations promptly and without damage.
Distribution channels can range from direct-to-consumer (D2C) models, where businesses sell directly to their end customers, to indirect models involving intermediaries like wholesalers and retailers. Implementing a flexible distribution strategy is crucial to adapting to unexpected disruptions, such as adverse weather conditions or transportation strikes.
Returns
The final component of SCM is handling returns, also known as reverse logistics. This stage involves processing customer returns, managing recalls, and replacing defective products.
An efficient return process not only boosts customer satisfaction but also offers businesses valuable feedback on product quality and areas for improvement. Companies must develop efficient return policies and logistics strategies to minimize losses and optimize inventory management.
Benefits of Supply Chain Management
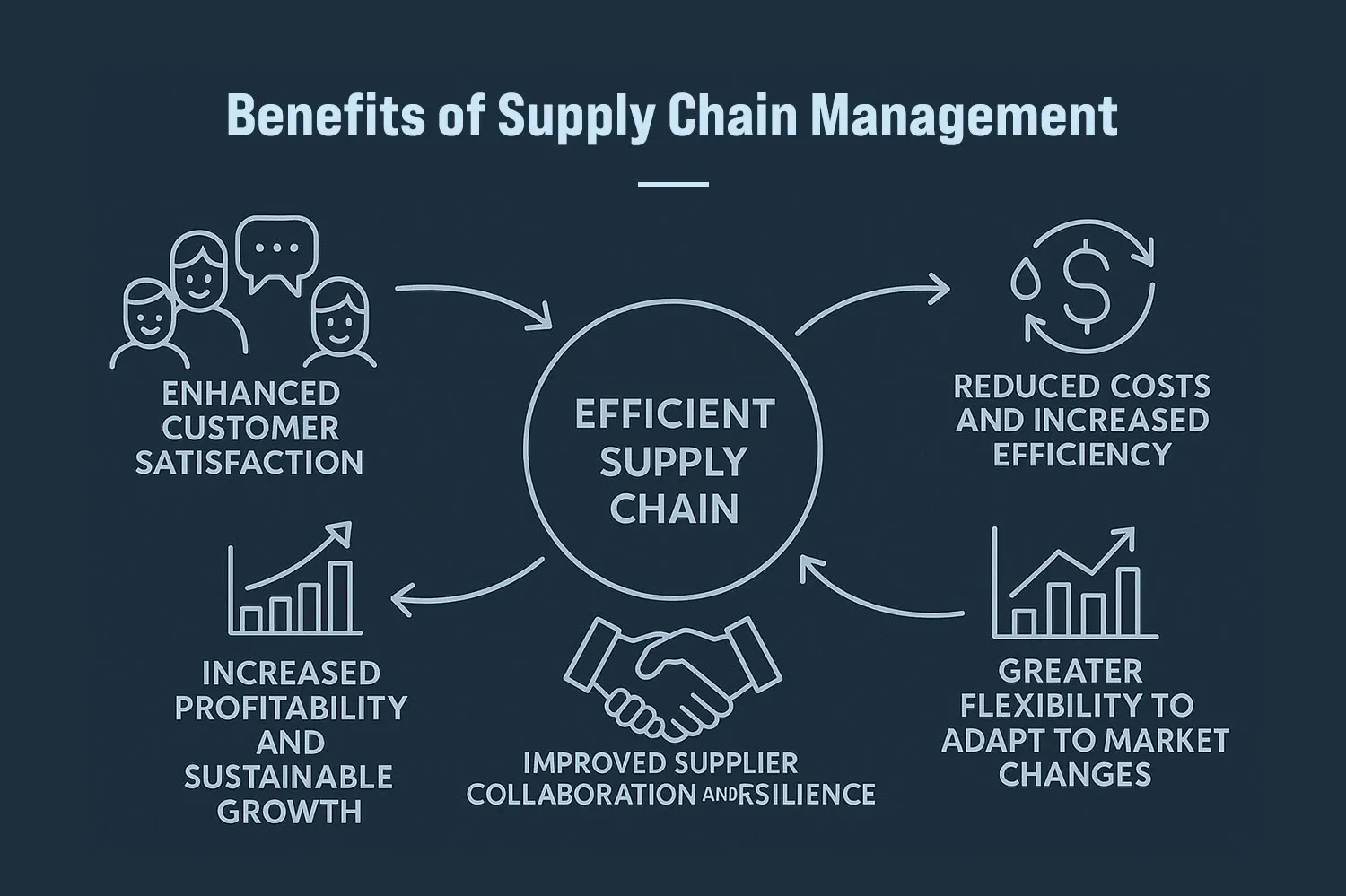
Efficient supply chain management (SCM) plays a crucial role in business success by optimizing processes, reducing costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction. Below are five of the most notable advantages of a well-optimized supply chain.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Communication
One of the most important benefits of SCM is improving customer relationships through better communication and transparency. Supply chain visibility solutions, such as real-time tracking, empower businesses to address disruptions like shipment delays or material shortages proactively.
By informing customers about possible delays and providing alternatives, companies foster trust and ensure a positive experience. Dependable SCM ensures timely product delivery, reducing customer complaints and enhancing satisfaction.
Reduced Costs and Increased Efficiency
A well-optimized supply chain helps businesses reduce operational costs by identifying inefficiencies at every stage, from procurement to distribution. By consolidating suppliers, automating production processes, and improving inventory management, companies can minimize waste, reduce storage costs, and optimize transportation.
Advanced SCM tools, including warehouse management systems (WMS) and transportation management systems (TMS), improve efficiency by optimizing logistics and refining delivery routes.
Improved Supplier Collaboration and Resilience
Strong relationships with suppliers lead to a more reliable and adaptable supply chain. Companies that invest in supplier relationship management (SRM) systems can track supplier performance, share real-time data, and address potential issues before they escalate.
This cooperation ensures a consistent flow of materials, lowers the risk of production halts, and enhances overall product quality. Businesses that prioritize supplier partnerships are better equipped to handle unforeseen challenges, such as raw material shortages or logistical disruptions.
Greater Flexibility to Adapt to Market Changes
A well-structured supply chain allows businesses to quickly respond to fluctuations in customer demand, supply shortages, and other market challenges. Companies with diversified supplier networks, flexible manufacturing processes, and advanced demand forecasting tools can swiftly adjust their operations to maintain product availability.
This flexibility is essential for maintaining a competitive edge, particularly in industries where consumer preferences and market trends shift rapidly.
Increased Profitability and Sustainable Growth
While improving supply chain management may require an initial investment, the long-term financial benefits are significant. Efficient SCM reduces unnecessary costs, enhances product quality, and strengthens customer loyalty—all of which contributes to increased revenue.
Moreover, businesses that implement sustainable and ethical supply chain practices not only minimize risks associated with unethical sourcing but also attract socially responsible consumers and investors.
How Does Supply Chain Management Work?
SCM operates through a series of structured steps that align production with market demand and optimize distribution. However, understanding the fundamental components of supply chain management is the first step.
SCM is primarily divided into three critical workflows:
- Product Flow: This involves the movement of goods through different stages, from raw material procurement to manufacturing, storage, and final delivery. Quality assurance checks are conducted at each step to maintain product integrity.
- Information Flow: The seamless exchange of data, including sales orders, purchase requests, inventory updates, and delivery tracking, plays a vital role in decision-making. Efficient management of information flow ensures that every component of the supply chain functions smoothly and effectively.
- Financial Flow: This encompasses billing, payments, credit terms, and overall financial management to ensure smooth transactions between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Effective financial oversight prevents disruptions in production and distribution.
Now that the key elements of SCM are clear, let’s explore how it functions.
Adapting Plans Based on Customer Demand
Understanding consumer needs is at the core of supply chain management. Through sophisticated market research and past sales trends, organizations dynamically calibrate inventory levels, while balancing resource allocation to prevent inventory surplus or unexpected shortages.
Optimizing Logistics for Efficient Distribution
Once products are ready, strategic distribution planning is essential to ensure timely delivery. Companies use key locations, such as regional warehouses and fulfillment centers, to store and distribute products efficiently. By analyzing data trends, businesses can anticipate seasonal fluctuations and improve logistical planning.
Developing Cost-Saving Strategies through Outsourcing
To maintain cost-effectiveness, companies assess different aspects of their supply chain and determine which functions can be outsourced. While outsourcing production or logistics can reduce expenses, businesses may choose to retain certain operations in-house for greater quality control and efficiency.
Using Data Analytics for Smarter Decision-Making
Data plays a crucial role in identifying inefficiencies, predicting customer preferences, and enhancing supply chain strategies. By evaluating consumer demand, production output, and inventory levels, businesses can refine their operations, reduce waste, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Why is Managing the Supply Chain Important?
Effective SCM is crucial for businesses to achieve operational efficiency, lower expenses, and meet customer expectations. Proper management helps streamline production, minimize delays, optimize inventory, and cut unnecessary expenses. It also enhances supplier relationships, improves logistics, and mitigates risks caused by market fluctuations or disruptions.
Additionally, a well-managed supply chain allows businesses to respond quickly to changing customer demands, maintain product quality, and gain a competitive edge in the market. By combining technology, data-driven insights, and strategic planning, organizations can attain long-term sustainability, profitability, and growth.
FAQs
Q1. Is supply chain management a high paying job?
Ans: Yes, supply chain management can be a high-paying career, especially for experienced professionals and those in leadership roles. Compensation varies depending on factors such as industry, geographic location, experience, and job role.
Roles like Supply Chain Manager, Logistics Director, and Chief Supply Chain Officer often offer competitive salaries with additional benefits. The field also provides opportunities for career growth and specialization, which can further increase earning potential.
Q2. Is supply chain management in demand?
Ans: Supply chain management remains a highly sought-after discipline, spanning diverse industry verticals including advanced manufacturing, global retail, healthcare innovation, and technology-driven sectors.
Global trade, eCommerce growth, and advancements in logistics and automation have increased the need for skilled supply chain professionals. Companies rely on efficient supply chain operations to stay competitive, making this career path a stable and lucrative choice with strong job prospects.
Summing Up
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is a vital and dynamic field that plays a crucial role in ensuring business efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction. As global trade grows and industries become more interconnected, the need for skilled SCM professionals continues to rise.
With opportunities for high-paying roles, career advancement, and job stability, SCM is an excellent career choice for those interested in logistics, operations, and strategic planning. By utilizing technology, data-driven strategies, and effective management practices, businesses can optimize their supply chains for sustained success and resilience.





