Differentiating Dropshipping vs. eCommerce

As you explore the world of eCommerce, you’ll quickly encounter two primary business models: traditional eCommerce fulfillment and dropshipping. Both have drawn thousands of new entrepreneurs into the digital marketplace, and while both allow you to sell products online, they have distinct differences that businesses should know about.
Similarly, how does one determine which model is right for a certain business? This article will break down what eCommerce and dropshipping are, compare their unique aspects, and provide insights to help choose the best path to meet business goals.
What is eCommerce?

Electronic commerce, commonly abbreviated as eCommerce, encompasses all digital transactions involving the exchange of products or services via web platforms, smartphone applications, or digital marketplaces. eCommerce businesses can take many forms, including online retail stores, digital product creators, or service providers.
This model allows businesses to reach a global audience, operate 24/7, and offer customers a seamless shopping experience with features like secure payment gateways, order tracking, and customer service.
India’s eCommerce industry is witnessing rapid expansion, with projections estimating the market will reach $325 billion by 2030, fueled by over 500 million online shoppers and growing internet accessibility. Additionally, India is expected to become the second-largest online consumer market by 2030, making eCommerce a highly lucrative space for entrepreneurs.
eCommerce businesses typically handle inventory, shipping, and branding themselves or through fulfillment centers. This hands-on approach provides complete control over every aspect of the business, but it also requires significant upfront investment in inventory and logistics.
What is Dropshipping?
Dropshipping is a distinct order fulfillment method that operates within the larger eCommerce framework. In this model, sellers don’t hold inventory or ship products themselves. Instead of stocking inventory, sellers pass customer orders directly to a third-party supplier, who then takes care of fulfillment and shipping.
Dropshipping is rapidly growing in India, with the market projected to reach USD 102.39 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 25.6%. The fashion segment was the largest revenue generator in 2023, while food & personal care is expected to be the fastest-growing category.
The dropshipping model removes traditional inventory costs and enables entrepreneurs to venture into online retail with minimal financial commitment, though it presents certain drawbacks including limited oversight of product standards, delivery processes, and brand identity management.
Think of dropshipping as a streamlined eCommerce strategy where the supplier handles much of the operational heavy lifting. Sellers focus on marketing, managing their online store, and curating products for their audience.
Dropshipping vs. eCommerce: Essential Differences
While both eCommerce and dropshipping operate in the digital space, they differ significantly in key areas of operations and marketing strategies. Below are the essential differences to help businesses choose the right model based on their goals and resources.
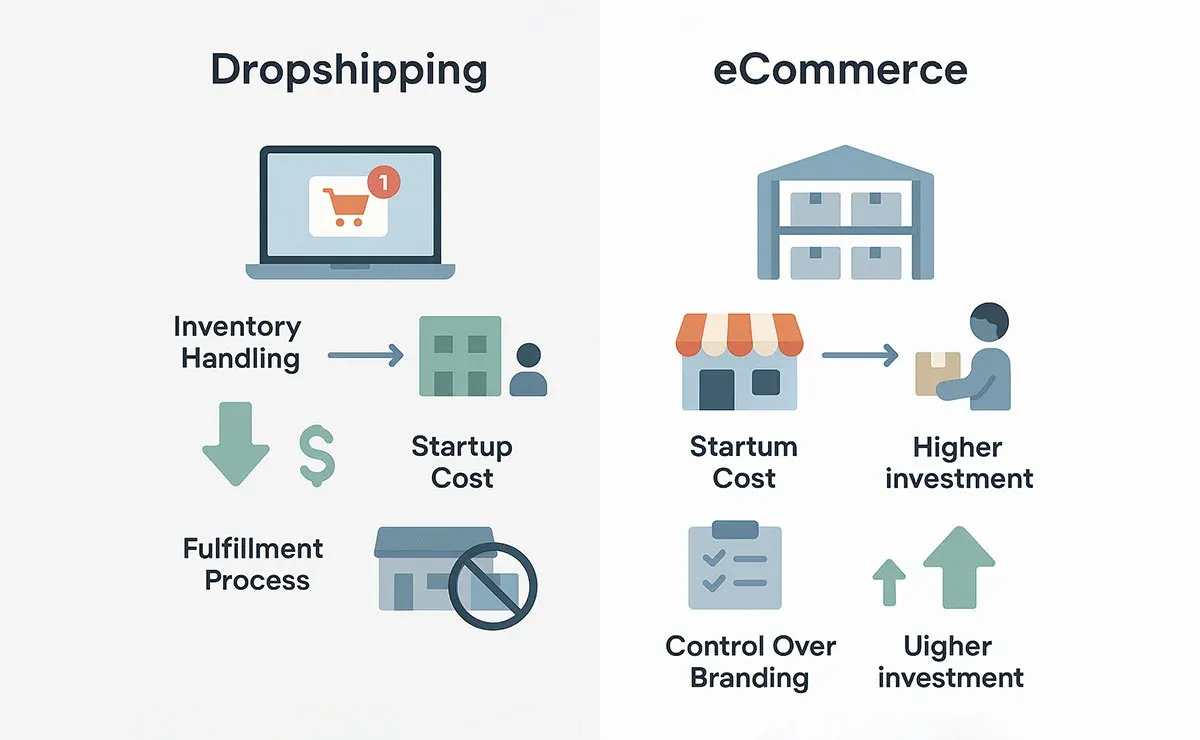
Inventory Management and Fulfillment
- eCommerce: Sellers handle fulfillment directly or use third-party logistics providers (3PLs). Note that eCommerce businesses own their inventory but may choose to outsource storage and fulfillment. It can be due to factors like faster shipping and more reliable delivery services.
- Dropshipping: Businesses don't own or maintain an inventory in this model, and since products are shipped directly from suppliers (often overseas), shipping times can be longer, and sellers have little control over delays.
Profit Margins
- eCommerce: Since sellers buy in bulk and store products, they often secure lower per-unit costs, allowing for higher profit margins. However, they also have to account for storage, shipping, and fulfillment costs.
- Dropshipping: Since products are purchased individually from suppliers, costs per unit tend to be higher, leading to lower profit margins compared to traditional eCommerce. Additionally, suppliers may charge additional fees for fulfillment and shipping.
Control Over Product Quality
- eCommerce: Business owners control product quality by sourcing from verified manufacturers, conducting quality checks, and ensuring consistency in product standards.
- Dropshipping: Sellers rely entirely on suppliers for quality control. If the supplier ships defective or low-quality products, it can negatively impact customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Branding and Customization
- eCommerce: Business owners can create unique branding, customize product packaging, and add promotional inserts, which help build strong customer loyalty.
- Dropshipping: Sellers typically use standard supplier packaging, offering little room for branding. Some suppliers allow white labeling, but options are limited.
Scalability
- eCommerce: Scaling requires increasing inventory, storage space, and logistics capabilities, which can be costly but offer long-term stability.
- Dropshipping: Easy to scale quickly since there’s no need to manage inventory, but profit margins may decrease due to rising competition.
Customer Experience & Brand Control
- eCommerce: Since you control product quality, branding, and fulfillment, you can offer a superior customer experience and build a stronger brand.
- Dropshipping: Customer experience depends on third-party suppliers, which can lead to quality inconsistencies, delays, and limited branding options.
Competition
- eCommerce: Businesses face competition from large retailers and marketplaces like Amazon and Flipkart but can differentiate through branding, exclusive products, and superior customer service.
- Dropshipping: Due to the low entry barrier, competition is extremely high, with many sellers offering identical products at minimal profit margins.
Risk Factor
- eCommerce: Requires investment in inventory, meaning higher financial risk if products don’t sell as expected.
- Dropshipping: Financial risk remains minimal since unsold inventory doesn't result in capital losses.
How to Build an eCommerce or Dropshipping Business
Launching a successful eCommerce business starts with selecting a profitable niche, choosing the right platform (like Shopify or Amazon), and deciding on a product sourcing method (dropshipping, wholesaling, or manufacturing).
A user-friendly website with strong branding builds credibility, while targeted marketing through SEO, paid advertising, and influencer partnerships drives traffic and sales. Excellence in customer service, backed by data analytics and efficient logistics, ensures customer satisfaction and retention.
As the business grows, strategic expansion of product lines and automation of key processes creates a foundation for sustained profitability in India's competitive digital marketplace.
Check out a more detailed article to understand how to start an eCommerce business in India?
Let's look at how to set up a dropshipping business in detail:
Step 1: Determine if Dropshipping is Right for You
Before diving in, assess whether dropshipping aligns with your business goals. This business model is best suited for individuals who:
- Wants to start a business with minimal financial risk and low initial investment.
- Possess marketing expertise or demonstrate willingness to develop these competencies.
- Wants to avoid managing inventory or handling shipments.
That said, dropshipping comes with challenges, including intense competition and lower profit margins. If you’re prepared to focus on branding, customer experience, and strategic marketing, dropshipping could be a great fit.
Step 2: Choose a Profitable Niche
A market niche represents a distinct consumer segment that enables focused customer targeting, making niche selection fundamental for differentiation in today's competitive digital marketplace.
How to Find a Niche:
- Follow Your Interests: Selling products that you are passionate about can make marketing more authentic and enjoyable.
- Market Research: Leverage analytics platforms such as Google Trends and Facebook Audience Insights to identify emerging market opportunities.
- Evaluate Competition: Research how many stores sell similar products. High demand with moderate competition is ideal.
- Consider Product Viability: Ensure the products are lightweight, easy to ship, and not overly saturated in the market.
Step 3: Conduct Competitor Analysis
Understanding your competitors can help you refine your strategy and identify gaps in the market.
Key Research Methods:
- Search Engine Assessment: Evaluate keyword rankings to identify top-performing competitors.
- Digital Analytics: Use platforms like SEMrush or Ahrefs to evaluate competitive website performance metrics.
- Social Media & Marketplaces: Check Amazon, Etsy, and eBay to evaluate demand and pricing.
- Competitor Websites: Study their product pages, customer reviews, and marketing techniques.
Keep track of your findings in a spreadsheet to compare pricing, customer engagement, and promotional tactics.
Step 4: Select a Reliable Supplier
Your supplier plays a vital role in the quality of your products and overall customer satisfaction. Partner with suppliers demonstrating:
- Consistent excellence in product quality and delivery efficiency.
- Transparent pricing with no hidden fees.
- Good customer support and responsive communication.
- Seamless technological integration with digital retail platforms for automated order fulfillment.
Step 5: Select Products and Set Pricing
Carefully curate products that align with your niche and attract your target audience.
Product Strategy Guidelines:
- Focus on products demonstrating strong market demand yet maintaining reasonable competition levels.
- Look for items with positive customer reviews.
- Avoid products with excessive shipping times or high return rates.
Pricing Strategy:
Factor in supplier costs, marketing expenses, and competitor pricing. Aim for a profit margin of 20-40% while keeping prices competitive.
Step 6: Build Your Digital Store
Your digital storefront serves as your brand's virtual headquarters - utilize intuitive and trusted platforms to establish a professional online presence.
Essential Elements of Your Store:
- User-friendly design: Choose a clean, mobile-responsive theme.
- Product descriptions: Use SEO-friendly content to highlight features and benefits.
- High-quality images: Optimize product photos for clarity and uniqueness.
- Optimized checkout: Install features like automated inventory management, live chat, and abandoned cart recovery tools to enhance the shopping experience.
Leverage AI tools like Shopify Magic to generate compelling product descriptions and enhance your images.
Step 7: Configure Your Business's Legal Framework
Select an appropriate legal entity structure that aligns with your business requirements, considering tax implications, liability exposure, and compliance obligations. Available structures include:
- Sole Proprietorship: Offers straightforward setup process but provides no personal asset protection.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): Offers liability protection and tax benefits.
- Corporation (C Corp or S Corp): Suited for expanding enterprises but involves complex regulatory requirements.
Seek professional legal guidance to determine the most suitable business structure for your venture
Step 8: Establish a Legal Business Structure
Set clear financial boundaries by creating a dedicated bank account for your business, enhancing bookkeeping, tax compliance, and fiscal management while projecting professional credibility.
Step 9: Develop Comprehensive Marketing Framework
Strategic marketing drives website traffic and revenue generation. Leverage various digital promotional channels, including:
- Social Media Marketing: Leverage platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok to promote your products.
- Email Marketing: Develop a subscriber database to facilitate promotional communications and strengthen customer bonds.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Optimize your store’s content to rank higher on Google search results.
- Paid Advertising: Run targeted ad campaigns across Google, Facebook, and Instagram to capture potential customers.
Step 10: Track Performance and Optimize Your Business
Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the success of your dropshipping business. Key performance indicators include:
- Conversion Metrics: Percentage of visitors completing desired purchase actions.
- Traffic Analytics: Identify primary channels driving the most visitor engagement.
- Customer Retention Rate: Measure repeat purchases and customer satisfaction.
- Ad Performance: Analyze return on investment (ROI) for paid advertising campaigns.
Regularly monitoring and adjusting these performance indicators enable strategic refinement and sustainable business expansion.
FAQs
Q1. Is eCommerce the same as dropshipping?
Ans: No, eCommerce is a broad category that encompasses all online selling models, whereas dropshipping is a specific fulfillment strategy within eCommerce. In traditional eCommerce, businesses manage inventory and fulfill orders themselves, whereas in dropshipping, a third-party supplier handles inventory and shipping on behalf of the seller.
Q2. Dropshipping vs eCommerce, which is better?
Ans: This choice depends on your budget, business goals, and risk tolerance. Dropshipping is ideal for beginners or those with limited capital since it requires minimal upfront investment and no inventory management. Traditional eCommerce, on the other hand, allows for greater control over branding, product quality, and profit margins but requires more investment in inventory and logistics.
Q3. Which business model is more profitable compared to dropshipping?
Ans: Several business models tend to be more profitable than dropshipping, including private labeling, wholesaling, and manufacturing custom products. Subscription-based businesses and digital products (such as online courses or software) also offer higher profit margins since they eliminate the costs associated with physical inventory and shipping.
Summing Up
Both eCommerce and dropshipping present exciting opportunities for aspiring entrepreneurs to enter the digital marketplace. Traditional eCommerce offers higher profit margins and better brand control but requires significant investment, while dropshipping provides a low-risk entry into online retail with minimal upfront costs.
Both models can lead to success in India's growing digital marketplace when executed with careful planning and strong customer focus. Consider your resources, long-term goals, and operational capabilities to choose the model that best aligns with your entrepreneurial vision.
Remember that as your business evolves, you can adapt your approach to incorporate elements of both models to maximize growth potential and market opportunities.





